This topic provides an overview of the basic structural elements of multidimensional data. Multidimensional data uses multiple, hierarchically structured dimensions to classify information. The following terms are commonly used to describe multidimensional data:
The table below describes the meaning of each term. The exact content of e.g. dimensions will differ from Analysis page to Analysis page.
Term |
Explanation |
|---|---|
Cube. |
A cube is the primary structure used to store and retrieve data within an OLAP database. In WebOffice, each analysis function is connected to a cube. The following cubes are available: •Event. •Collection. •Purchase. •Card Transactions. A cube contains measures and dimensions. |
Dimension. 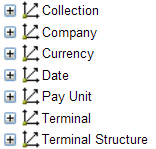 |
A dimension provides a way to organize data according to independent logical groups. This is the highest structure within the multidimensional data model. It is helpful to think of a dimension as a ‘category of information’. For example, a dimension may include the logical groups Date, Terminal, or Hardware Unit. A dimension consists of hierarchies and attributes.
The image shows Dimensions for Collection Analysis. |
Hierarchy. 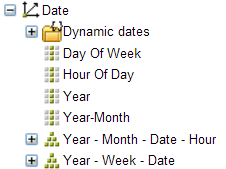 |
Some dimensions contain hierarchies to group data hierarchically. A typical example is the Date Dimension that contains several hierarchies, e.g. Year->Month->Date->Hour. This hierarchy contains four levels. When creating reports with these dimensions it may not always be clear what the data is about. E.g., you will see a column with the day numbers of a month where purchases are made when you use only Hour Of Day. Mostly the header will make clear what the selection was when you created the report. |
Attribute. |
An attribute is a property of a dimension. For the Terminal dimension, the Terminal ID and the Location are two different attributes. |
Member. |
A member is an element of a dimension, e.g. a specific terminal or a specific event code. |
Measure. 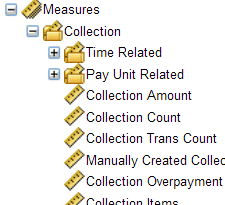 |
A measure is a numeric value that is analysed. Measures are aggregated based on dimension selection. Example of measures: •Event Count. •Purchase Amount. |